Rohail Asim
I am a PhD Candidate in Computer Science at the Courant Institute of Mathematical Sciences, New York University advised by Professor Yasir Zaki and Professor Lakshminarayanan Subramanian . My research interests include Computer Networks, Artificial Intelligence, and Sustainable Computing. I completed my BS in Computer Science in 2019 from Lahore University of Management Sciences (LUMS) where I also worked as a Research Assistant at the Technology for People Initiative (TPI) before joining NYU. I am currently working on multiple projects within the domain of Computer Networks especially involving the analysis and advancement of Congestion Control protocols for next generation wireless networks.
Media Coverage
View all coverage →Major media outlets worldwide that have featured my research at NYU include The Times, Nature, New Scientist, and more.
Projects

Enabling High Bandwidth Applications over 5G Environments
A new low-latency framework tailored for AR/VR over 5G networks
SONIC: Connect the Unconnected via FM Radio & SMS
Delivers web access to remote regions using FM radio and SMS with no internet.
Rethinking Congestion Control for 5G
A deep analysis of congestion control algorithms in high-speed 5G environments

Towards a world wide web without digital inequality
Improve web access for low-end devices in underserved areas
Rethinking homework in the age of AI
Analysis of ChatGPT’s impact on academic integrity and student performance
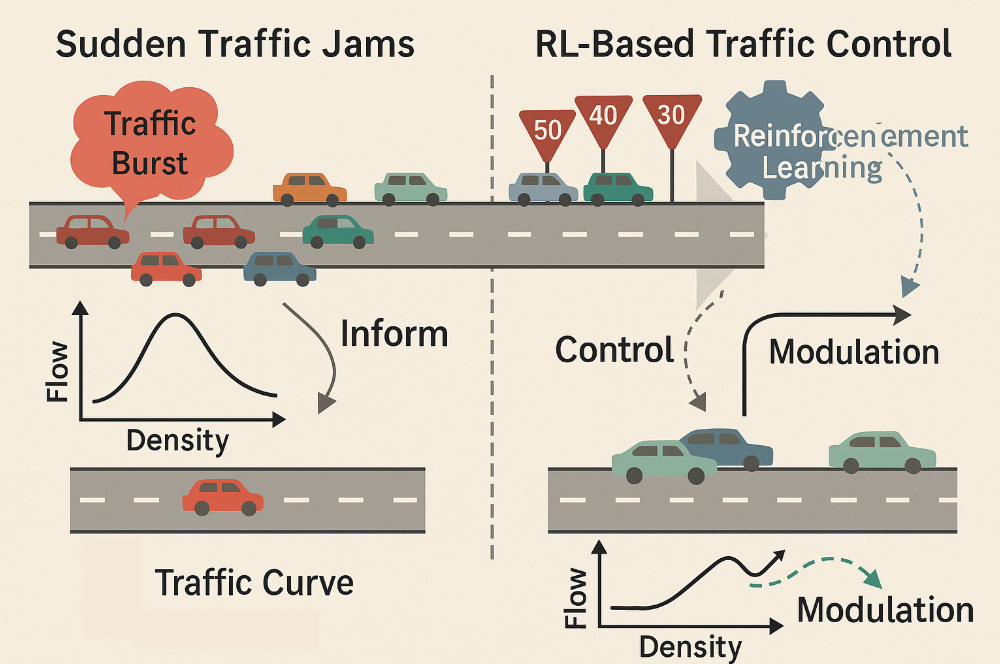
Understanding and Mitigating Traffic Jams Using Edge AI
Use Edge AI and RL to detect and prevent traffic jams without new infrastructure

Sustainable AI
Enabling sustainable AI data centers under environmental and economic policies
Selected Publications
[1] R Asim, A Bhardwaj, A Sathiaseelan, Y Zaki, and L Subramanian Modeling Economic Viability for Scalable AI Deployment in Emerging Regions
Accepted at PACMI'25: Proceedings of the 2025 SOSP Workshop on Practical Adoption Challenges of ML for Systems
[2] R Asim, L Subramanian, and Y Zaki Impact of Congestion Control on Mixed Reality Applications
EMS '24: Proceedings of the 2024 SIGCOMM Workshop on Emerging Multimedia Systems
[3] A Pandey, R Asim, K Mengal, M Varvello, and Y Zaki SONIC: Connect the Unconnected via FM Radio & SMS
Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on emerging Networking EXperiments and Technologies
[4] R Asim, A Sathiaseelan, A Chatterjee, M Lal, Y Zaki, L Subramanian The GAIUS Experience: Powering a Hyperlocal Mobile Web for Communities in Emerging Regions
Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Information & Communication Technologies and Development
[5] R Asim, A Bhardwaj, L Subramanian, and Y Zaki Enabling High Bandwidth Applications over 5G Environments
Demo in ACM SIGCOMM 2024
[6] A Pandey, R Asim, M Varvello, Y Zaki Connecting the Unconnected Using FM Radio
Demo in ACM SIGCOMM 2024
[7] A Pandey, R Asim, M Varvello, L Subramanian, Y Zaki Towards Faster Web in Developing Regions
Demo in ACM SIGCOMM 2024
[8] H. Ibrahim, F. Liu, R. Asim, T., Y. Zaki et al. Perception, performance, and detectability of conversational artificial intelligence across 32 university courses
In Scientific Reports 13 (1), 12187
[9] H Ibrahim, R Asim, F Zaffar, T Rahwan, Y Zaki Rethinking homework in the age of artificial intelligence
IEEE Intelligent Systems 38 (2), 24-27
[10] M Chaqfeh, R Asim, B AlShebli, MF Zaffar, T Rahwan, Y Zaki Towards a world wide web without digital inequality
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 120 (3), e2212649120
[11] H Ibrahim, R Asim, M Varvello, Y Zaki I Tag, You Tag, Everybody Tags!
In Proceedings of the 2023 ACM on Internet Measurement Conference, 561-568
[12] Y Zaki, R Asim, M Khan, S Iyer, T Ahmad, T Potsch, L Subramanian ALCC: Migrating Congestion Control To The Application Layer In Cellular Networks
Journal of Systems Research 2 (1)